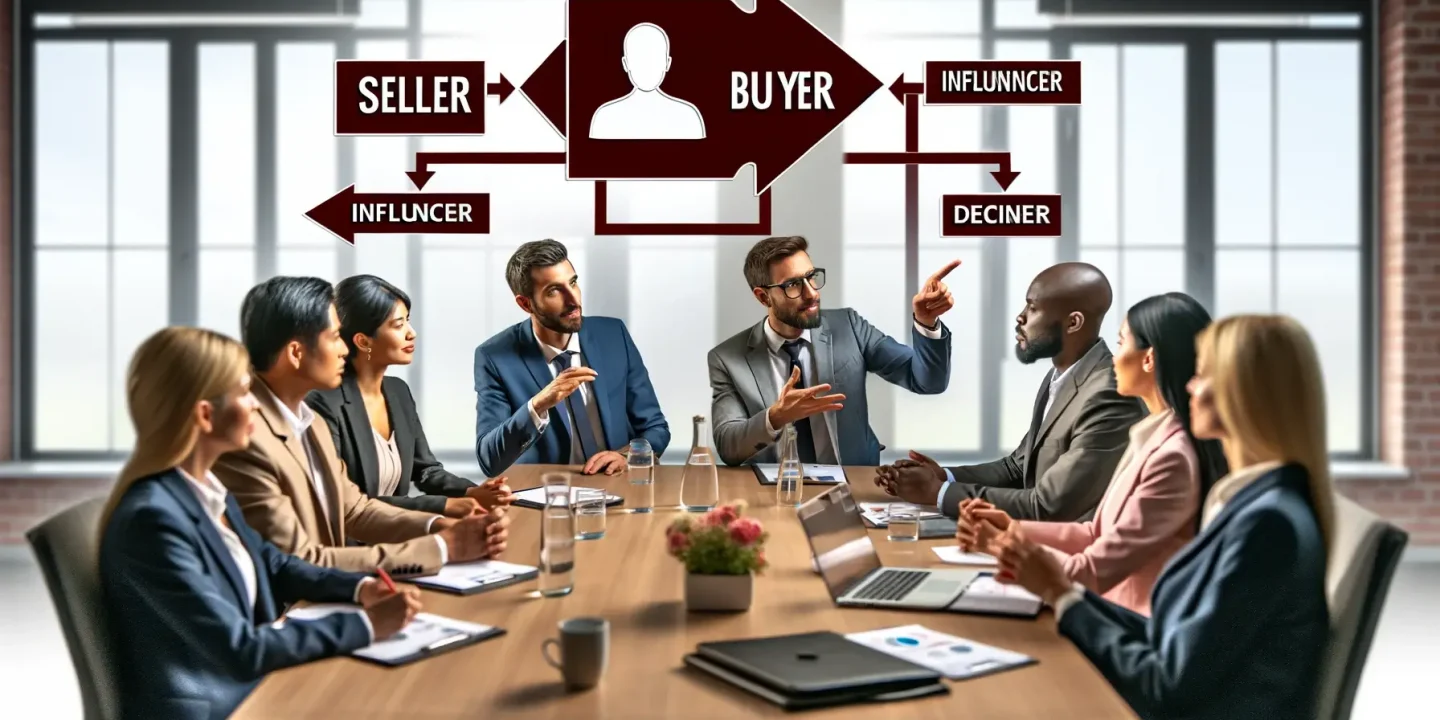
Who takes the Purchasing Decision: A Dive into Marketing Theory with Philip Kotler, a renowned figure in marketing, offers a framework that is particularly useful in understanding the dynamics of organizational buying behavior, which can be applied effectively in procurement.
According to Kotler’s theory, there are several roles that individuals within an organization may assume during the purchasing decision making process. These roles are part of what he refers to as the “buying center,” a concept he elaborates on in his seminal work, “Marketing Management.” The buying center consists of all the individuals and groups who participate in the purchasing decision process.
This blogpost does not adress the consumer purchasing decision process.
Who tales the Purchasing decision?
Who takes the Purchasing Decision – The Roles in the Buying Center
- Initiators:
- Initiators are the ones who first suggest buying a particular product or service. They are the catalysts for the procurement process, identifying a need or a problem that requires a solution through purchasing. In a manufacturing setting, this could be an engineer who sees the need for a new machine that could increase production efficiency.
- Influencers:
- Influencers are people who directly or indirectly affect the buying decision. They might not have the final say, but their opinions are valued because of their expertise or specific knowledge about the product or its application. For example, the IT department might influence the procurement of new software by advising on compatibility and security issues.
- Deciders:
- Deciders are those who ultimately make the buying decision, whether or not they themselves use the product. They have the power to approve or reject suppliers and make the final purchasing decisions. In many cases, this could be the senior management or the head of a particular department, depending on the size of the expenditure.
- Buyers:
- Buyers are the individuals who handle the procurement process. They are responsible for arranging the terms of the purchase and ensuring that the transaction is completed. They are typically procurement managers or purchasing agents who have been empowered to negotiate prices and terms with suppliers.
- Users:
- Users are the ones who will actually use the product or service in question. Their feedback can be crucial in determining the specifications that are required and in evaluating the performance of the purchased goods or services after implementation. Users can often initiate the buying process or influence decisions by reporting needs or problems.
- Gatekeepers:
- Gatekeepers control the flow of information in the buying process. They can include secretaries, technical experts, or anyone who has control over what information reaches members of the buying center. They play a crucial role in keeping the procurement process efficient by filtering out irrelevant information or vendors.
Applying Kotler’s Framework to Procurement
Understanding these roles helps procurement professionals navigate internal dynamics and manage relationships effectively both within the organization and with external suppliers. By identifying who the influencers, deciders, and users are, procurement can tailor their strategies to address the concerns and needs of these key stakeholders more effectively.
Furthermore, leveraging the insights provided by users and influencers can enhance the alignment of the procurement function with the strategic goals of the organization, ensuring that purchases contribute directly to organizational efficiency and effectiveness.
Kotler’s framework underscores the complexity of organizational buying behavior and highlights the need for a strategic approach in managing procurement activities. By understanding and addressing the roles within the buying center, procurement professionals can optimize their interactions and improve the outcomes of their buying decision process.
Case Study: Solectron in Norrköping
Solectron, a former contract manufacturer of electronic products, offered services ranging from assembly to design and New Product Introduction (NPI). In the example with Solectron and their customer, the fictional British company Electronic Ltd, illustrates how a deep understanding of the above roles can streamline both marketing and sales.
Electronic Ltd decided at its inception to focus on research and development as well as marketing, while manufacturing would be outsourced. In this company, the founders fill the roles of initiators and influencers, while the production and purchasing manager acts as the decider. Purchases are administered by an employee from the finance department, and the users of the products are primarily on the sales side.
Strategic Approaches
For Solectron, it becomes essential to adapt its sales strategies to these roles. An effective way is to appoint a key account manager who can build high-level relationships with Electronic Ltd’s management and a team of specialists who collaborate directly with the production and purchasing manager to ensure that all needs are efficiently met.
Lessons and Strategies
By consciously analyzing and understanding the customer’s internal purchasing decision making processes, Solectron and similar suppliers can create stronger and more successful collaborations. This strategy not only facilitates sellers to tailor their offerings but also gives purchasers insights into how they can influence and optimize their own internal processes.
Summary – Who takes the Purchasing Decision
In summary, this example demonstrates the importance of understanding and adapting to the various roles within an organization to successfully manage supplier relations and streamline procurement decisions. This approach can significantly improve both supplier and customer relations, leading to better business outcomes.
Learn more about sourcing and purchasing decision.
If you want to learn more about the sourcing process we recommend the bundle of courses called: The sourcing engine room – a modern sourcing process. In the bundle you will learn the skills and strategies needed to excel in the sourcing process, from finding the best suppliers to negotiating contracts and managing risk.
Our course is designed to be accessible and engaging, with interactive lessons that allow you to learn at your own pace and test your knowledge along the way. You’ll have access to industry experts and real-world case studies that will help you understand the sourcing process in depth and apply your new knowledge to your own work. If you want to learn more about “Who takes the Purchasing Decision” we recommend Kotler’s book.
If you only want to learn about the basic sourcing process we recommend the course Sourcing Process 1.
Note: Illustration to the blogpost “Who takes the Purchasing Decision” is created by Chat-GPT on May 1, 2024.